How AI will impact jobs has become a topic of great interest and concern as the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence continue to reshape many industries. As we stand on the cusp of an era dominated by supercharged language model AI, we must understand how these developments will affect human labour and the future of work.
In this post, we will cover the evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its impact on jobs, exploring generative AI algorithms and large language models that have accelerated technological change. We will also discuss factors influencing the adoption of AI across various sectors.
We will compare recent papers and opinions from commentators and industry insiders covering which jobs are most at risk due to increased productivity from machine learning systems. By examining methodologies for determining risk levels and listing vulnerable occupations, you can better prepare yourself for potential job losses, or at least job changes, caused by generalised artificial intelligence technologies.
Lastly, we will address economic disparities arising from widespread AI adoption. This includes challenges faced by younger generations entering a workforce transformed by automation as well as influencing factors for labour productivity outcomes resulting from such shifts in technology use.
This comprehensive exploration aims to provide valuable insights into the current state of affairs surrounding the ever-growing influence of artificial intelligence on our lives and livelihoods – particularly focusing on its implications for job markets worldwide.
The Evolution of AI and Its Impact on Jobs
Artificial intelligence (AI) has evolved exponentially in recent years, with generative AI and large language models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT becoming more advanced. This rapid development raises concerns about the potential impact of AI on the future of work across various job sectors, as its adoption and integration could disrupt numerous occupations.
According to a report by Pew Research Center, Americans have mixed feelings about artificial intelligence. While some are excited about the benefits of AI, others are concerned about its impact on society.
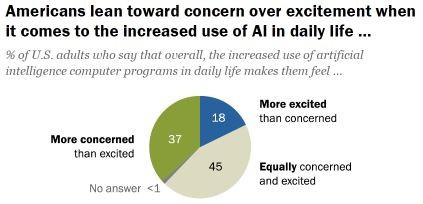
The report showed that more Americans were actually more concerned than excited by the prospects of AI. However, the majority (nearly half) of respondents are equally concerned and excited.
Those concerned worry about potential job losses, privacy and the prospect that AI technology will surpass human skills someday. Others are also concerned about the misuse of AI, that human connection will be lost, and that humans will place too much reliance on AI.

For those more excited about the prospect of AI opportunities, they mention such things as the hope of improvements to society, time savings and efficiencies to daily life, and how AI systems might make things safer at work.
Generative AI and Large Language Models
Generative AI, a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new content or data, is transforming many industries by automating tasks such as content creation, design work, and even drug discovery. Examples include OpenAI’s GPT-4 or specific AI writing tools like Content at Scale and Jasper, which can generate human-like text based on given prompts.
As these technologies become more sophisticated, they can potentially replace jobs (or at least a significant portion) that involve repetitive tasks or require extensive knowledge. For further reading to see how AI tools are already used in the content creation industry, see this article.
Large language models (LLMs), like GPT-4 from Open AI or Bard from Google, are designed to understand the context better than previous iterations of natural language processing tools. These LLMs can perform a wide range of tasks, including translation services and summarisation services for articles or reports, without any specific training required for each task.
Factors Influencing the Adoption of AI

Economic Factors: Companies may adopt artificial intelligence solutions if it leads to cost savings through increased efficiency or reduced labour costs.
Social Factors: Public opinion towards automation will significantly determine how quickly businesses embrace this technology. Positive attitudes may lead to faster adoption, while negative sentiments may slow it down.As stated in this article, you can browse your selection of available deals on smartphones and top brands and explore the cell phone service plans that best suit your needs.
Regulatory Factors: Governments can either encourage or hinder the development and deployment of AI technologies through legislation, subsidies, or restrictions. For example, policies that protect workers’ rights could limit the extent to which companies can automate roles.
The Need for Regulation
In a recent CBS 60 Minutes interview with Google (“Alphabet”) CEO Sundar Pichai, it was noted that even technology companies at the cutting edge of artificial intelligence have varying views. Some staff are excited about AI’s potential and want to accelerate efforts. Some advise slowing the progress so that society and governments have time to catch up, understand its potential impact, and regulate accordingly.
An Open Letter
There were also recent calls from industry experts to slow down the exponential progress of the advancing technology. A group of industry executives and artificial intelligence experts recently called for a six-month pause in developing more powerful systems than OpenAI’s newly launched GPT-4.
They have issued an open letter now signed by over 27,000 people (April 2023), reportedly including industry heavyweights such as Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla, SpaceX and Twitter; Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI; Sundar Pichai, CEO of Alphabet; Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft; and Steve Wozniak, the co-founder of Apple.
The letter calls out the potential risks to individuals and society. The group is urging for a pause on advanced AI development until shared safety protocols are developed by independent experts and for developers to work with policymakers on governance.

In particular, for years, the question of AI’s evolution and its consequences on the future of work has been debated more intensely as technology advances. With this in mind, we now consider the various opinion on which jobs are most at risk due to the implementation of AI technologies.
Which Jobs Are Most at Risk?
The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence have raised concerns about the potential impact on various job sectors. There are varying opinions on what percentage of the job market will be impacted and the extent to which such impact will only replace part of one’s occupation or all of it.
One thing in agreement across all studies and commentators is that LLMs such as GPT-4 exhibit traits of general-purpose technologies, indicating that they could have considerable economic, social, and policy implications.
a) CBS 60 Minutes Interview with Google CEO Sundar Pichai
Some jobs will be replaced and more jobs added, but the greatest impacted category is job changes. Assisted by AI and automation, more than two-thirds of roles will have their job definitions changed (not fully replaced). Knowledge workers like writers, accountants, architects and even software engineers are particularly exposed.
b) Goldman Sachs Research Paper:
The paper (March 2023) summarised that generative AI (like GPT-4) could drive a 7% increase in Global GDP over a 10-year period. Such AI platforms could impact global employment markets, exposing around 300 million full-time equivalent jobs to AI automation.
From a database of over 900 occupations, the paper estimates roughly two-thirds of occupations are exposed to some degree of AI automation. One-quarter of all work-related tasks in the US and Europe are predicted to be automated. However, it was noted that although some of the tasks within these occupations could be replaced, this would not all translate to complete job replacements.
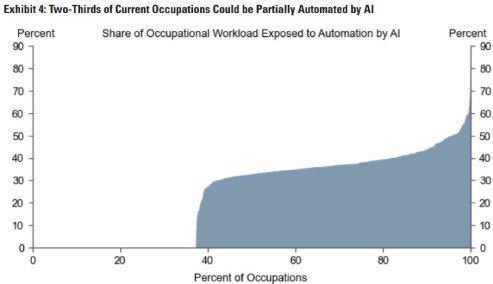
The most impacted jobs from AI automation were predicted to be among administrative/clerical, professional, legal and management occupations. Less affected were jobs in construction, maintenance, machinery operators and craft and related trades.
c) Cornell University Study
A comprehensive study analysing over 1,000 different occupations has shed light on which jobs are most susceptible to AI technology disruption. By assessing the effects of AI on general tasks and job-specific tasks, researchers were able to identify over 80 occupations that could be significantly affected.
The key metric summarised from the study was that at least 19% of jobs were predicted to have more than half of their tasks replaced by AI innovation. 80% of the workforce could also see at least 10% of their tasks replaced by AI, indicating a widespread impact across most, if not all, industries.
To a varying extent, human employees’ tasks could be replaced by AI, leaving workers to change their roles and re-skill in new areas.
For an excellent summary of the study, see the video further below from Coin Bureau, where Guy takes you through the main points and some of his thoughts. Below are some of the highlights from the study showing which occupations are more likely to be impacted.
I) Analysis Methodology for Determining Risk Levels
Researchers employed a two-fold technique to gauge the potential concern connected with each job. First, they examined how AI would affect general tasks such as data processing or information search. Second, they assessed how specific applications of AI could disrupt particular job functions within each occupation.
This analysis allowed them to assign an “AI exposure score” for each role based on its vulnerability to automation and displacement due to advances in artificial intelligence technologies.
II) List of Vulnerable Occupations
According to the study’s findings, some of the most vulnerable occupations include white-collar jobs requiring a higher education level. Those holding a Bachelor’s degree, Master’s degree and other professional degrees are actually more exposed to AI-powered software.
Ironically, high-skilled jobs like software engineering and writing/authoring are some of the highly impacted areas. Specific jobs with high exposure include:
Programmers
Accountants
Auditors
Financial analysts
Legal secretaries
As someone with training and experience in both the Finance and Legal sectors, I can see a large percentage of the human labour in associated tasks being replaced by a more efficient AI process.
In the Finance sector, daily, weekly and monthly management or financial reports could be produced quickly by an efficient AI, with the human employees diverting their time to more “value-added” or critical thinking tasks.
During my Bachelor’s in Law, I recollect researching, reading and summarising case law as time-consuming. AI would bring significant efficiency to many jobs in the Legal sector.
Here are some of the many jobs with exposure to AI technologies that the study predicted based on their methodology (one based on Human raters, the other based on GPT-4’s own assessment – both yield similar results).
There was a broad impact predicted across nearly all industries and sectors. However, the common theme across both assessments is that most jobs requiring some form of data or information processing will be impacted:
Top 10 as per Human Raters (of over 80 occupations impacted)

Top 10 as per GPT-4 (of over 80 occupations impacted)

III) List of Occupations Without Any Exposed Tasks
Here are some of the occupations the study found without any risk of exposure to AI. Some are expected for obvious reasons, like sports competitors, while others require human hands (or senses), like cooking or critical thinking.
Surprisingly, more manual tasks, like brick masons, carpenters and plasterers, were seen as safe from being impacted by AI advancements.

d) Proactively Adapting to AI Advancement
As acknowledged in these studies, it is essential for professionals working in the industries impacted to be aware and proactively adapt their skills to work alongside emerging AI technologies effectively.
This may involve continuous learning, upskilling, or even transitioning into new jobs where human intelligence remains indispensable. It might also mean employers adjust the nature and remit of current jobs to accommodate this re-skilling, incorporating further “value-added” tasks that human workers can bring to the table alongside their AI skills.
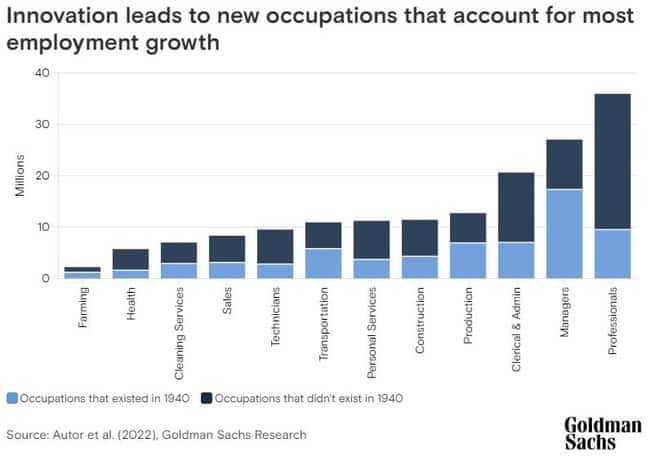
It’s not the first time, nor will it be the last time, that continuous innovation leads to new jobs (or at least a definition change) that accounts for most long-term employment growth. This graph from the Goldman Sachs Research paper noted that 60% of today’s workers are employed in occupations that didn’t exist in 1940.
The implication is that a significant portion (greater than 85%) of employment growth over the last 80 years is due to technological advancements creating more jobs and opportunities across existing and new industries. The likes of digital marketers, web designers or software developers didn’t exist 80 years ago!
Key Takeaway:
While the potential disruption to specific roles can be considerable, it is crucial to recognise that AI adoption also presents new jobs and increased productivity opportunities. By staying informed about the latest advancements in artificial intelligence and adapting accordingly, individuals can mitigate the risks associated with AI’s impact on their careers.
The findings of various studies demonstrate that certain occupations are more vulnerable to automation and AI than others. Therefore, understanding the economic implications of advancing AI technologies is critical to ensure just results for everyone.
Economic Disparities Caused by AI Adoption

As artificial intelligence advances, it may lead to massive economic disparities in the job market between those who can adapt their skills to work alongside these technologies versus those whose jobs become obsolete.
Social, economic, and regulatory factors will play a significant role in shaping actual labour productivity outcomes resulting from the increased use of AI.
a) Challenges Faced by Younger Generations
The younger generations will likely face unique challenges as they enter the workforce amidst rapid technological advancements. As McKinsey Global Institute’s research suggests, there is an increasing need for human workers with advanced technical skills and digital literacy.
Despite having access to educational institutions that could teach essential digital skills, many underprivileged students remain unprepared for the demands of future job markets.
Lack of access: Many students in underprivileged areas lack access to proper resources or educational institutions that teach essential digital skills required for future job markets.
Skill mismatch: The rapidly changing nature of technology creates a skill gap where many graduates are unprepared for the demands of modern workplaces.
Gig economy: A growing reliance on short-term contracts and freelance work could make it difficult for young professionals to secure stable employment with long-term career prospects.

b) Influencing Factors for Labour Productivity Outcomes
The impact of AI adoption on labour productivity depends on several social, economic, and regulatory factors. Understanding these elements can help businesses and policymakers navigate the potential consequences effectively:
Education and training: A well-designed education system that focuses on developing essential skills, such as digital or AI skills, problem-solving abilities, and adaptability, can help workers stay relevant in the age of AI. The World Economic Forum’s 2016 paper refers to it as the 4th industrial revolution, and consistent with the prior industrial revolution, emphasises the importance of lifelong learning to ensure continuous skill development.
Social safety nets: Governments should consider implementing robust social safety nets such as unemployment benefits, retraining programs, or universal basic income to support those affected by job displacement due to AI adoption.
Inclusive growth policies: Policymakers must prioritise inclusive growth strategies that promote equal opportunities for all citizens regardless of their socio-economic background. This could involve investing in infrastructure projects or providing financial incentives for businesses operating in underprivileged areas.
Labour market regulations: Updating labour laws and regulations is crucial to protect workers’ rights while encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship. For instance, governments may need to reconsider traditional employment contracts given the rise of gig economy jobs.

Key Takeaway:
As AI advances, it may lead to economic disparities between those who can adapt their skills and those whose jobs become obsolete. Younger generations face unique challenges entering the workforce amidst rapid technological advancements, including a lack of access to quality education or training programs that prepare them for this new reality.
Policymakers must prioritise inclusive growth strategies and update labour laws to protect workers’ rights while encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship in the age of AI.
FAQs
What is the impact of AI on jobs?
The impact of AI on jobs includes increased efficiency, productivity, and cost savings. However, it also leads to job displacement as specific tasks become automated. While some occupations may decline or disappear, new opportunities arise in fields such as AI development and machine learning.
Will AI Replace Content Writers?

The impact of artificial intelligence on content writing is undeniable. With many AI content writing software available today to help automate specific tasks and improve productivity, it is yet to be determined, or just a matter of time, whether or not AI will fully replace content writers. For further reading, see: Will AI Replace Content Writers & Bloggers?
Conclusion
AI has had a considerable influence on the way we work worldwide and will continue to do so. Various commentators and studies have predicted that anywhere from half to two-thirds of occupations could be partially automated by AI in the coming years.
While most industries and sectors are impacted, and specific jobs are more affected than others, it is important to recognise that there will be winners and losers as this technology continues evolving. We must also understand the economic disparities caused by its adoption to ensure fairness for all workers regardless of their industry or role.
The exact impact on the future of work remains uncertain. Still, one thing is clear: individuals and companies must take responsibility for understanding how AI will impact the job market and shape their individual career goals and business strategies accordingly. Exercising some human intelligence which brought us to this stage, will guarantee our individual survival and ensure that we thrive in a fast-changing job market.
What are your thoughts on how AI will impact jobs and change the future of work? Are you already feeling some impact, seeing AI replace jobs, or maybe even creating job opportunities? Add your comments in the section below.
Author: Darrell Chau
Date: 25 April 2023
Want more posts like these? If so, sign up for the newsletter using the blue icon above.
